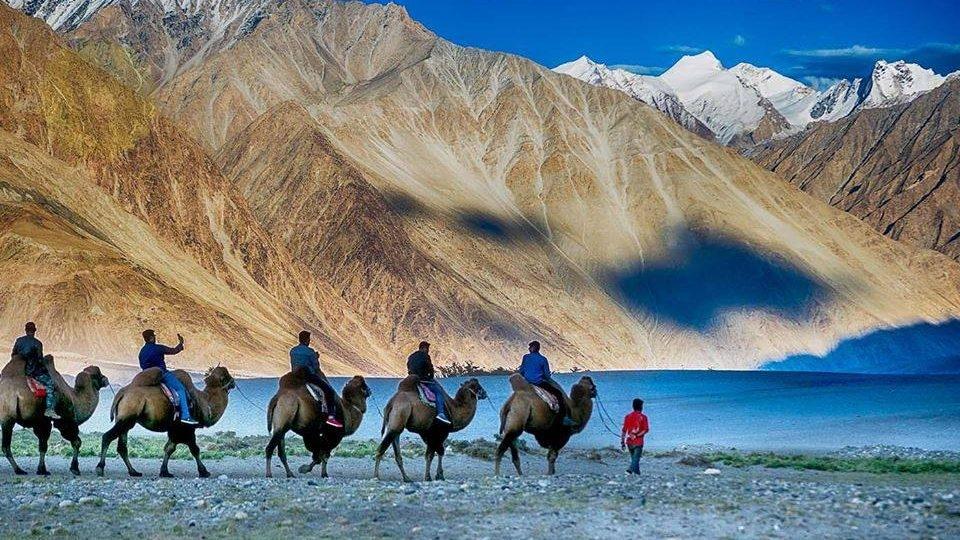
Ah, Ladakh! The very name conjures up images of rugged mountains, serene monasteries, and vast open landscapes. Let's dive into this fascinating region:
**Ladakh: The Roof of the World**
Ladakh, often referred to as "the roof of the world" or "the land of high passes," is a remarkable region in northern India. Here are some key points about Ladakh:
1. **Geography and Borders**:
- Ladakh is situated in the northern and eastern part of the Indian subcontinent, bordering Tibet (China), Pakistan, and the Indian state of Himachal Pradesh.
- It extends from the Siachen Glacier in the Karakoram range to the north, all the way to the main Great Himalayas in the south.
- The eastern end includes the uninhabited Aksai Chin plains, which are claimed by India but have been under Chinese control.
- Ladakh's strategic location at the crossroads of important trade routes historically contributed to its significance⁴.
2. **Administration and Status**:
- Since October 2019, Ladakh has been administered as a union territory of India.
- The region comprises two districts: Leh and Kargil.
- Leh, the largest town, serves as the district headquarters.
- Ladakh's official languages are Hindi and English, while Ladakhi, Purgi, Shina, and Balti are also spoken⁴.
3. **Culture and Religion**:
- Ladakh is a melting pot of diverse cultures and religions.
- The main religious groups include Muslims (mainly Shia), Buddhists (primarily Tibetan Buddhists), and Hindus.
- Monasteries dot the landscape, and Ladakh is famous for its vibrant festivals and rich cultural heritage⁴.
4. **Tourism and Adventure**:
- Since the 1970s, the Indian government has actively promoted tourism in Ladakh.
- Visitors are drawn to its high-altitude landscapes, pristine lakes, and ancient monasteries.
- Adventure enthusiasts flock here for trekking, river rafting, and mountaineering.
- Leh Palace, perched atop a hill, offers panoramic views of the city and surrounding mountains².
5. **Climate and Lifestyle**:
- Ladakh experiences a cold and dry climate, with extreme temperature variations.
- The main sources of livelihood are agriculture, animal husbandry, and tourism.
- The region's sparse population includes pastoral Changpa nomads who inhabit the mountain slopes⁴.
6. **Remembering Chang La**:
- Speaking of mountain passes, one of the most famous is Chang La.
- Chang La, at an elevation of 5,360 meters (17,590 feet), is known for its breathtaking views and challenging terrain.
- It's a gateway to the Nubra Valley and Pangong Lake, both must-visit destinations in Ladakh³.
So, whether you're dreaming of exploring ancient monasteries, embarking on a thrilling trek, or simply soaking in the awe-inspiring landscapes, Ladakh awaits with open arms!
**Ladakh: The Roof of the World**
Ladakh, often referred to as "the roof of the world" or "the land of high passes," is a remarkable region in northern India. Here are some key points about Ladakh:
1. **Geography and Borders**:
- Ladakh is situated in the northern and eastern part of the Indian subcontinent, bordering Tibet (China), Pakistan, and the Indian state of Himachal Pradesh.
- It extends from the Siachen Glacier in the Karakoram range to the north, all the way to the main Great Himalayas in the south.
- The eastern end includes the uninhabited Aksai Chin plains, which are claimed by India but have been under Chinese control.
- Ladakh's strategic location at the crossroads of important trade routes historically contributed to its significance⁴.
2. **Administration and Status**:
- Since October 2019, Ladakh has been administered as a union territory of India.
- The region comprises two districts: Leh and Kargil.
- Leh, the largest town, serves as the district headquarters.
- Ladakh's official languages are Hindi and English, while Ladakhi, Purgi, Shina, and Balti are also spoken⁴.
3. **Culture and Religion**:
- Ladakh is a melting pot of diverse cultures and religions.
- The main religious groups include Muslims (mainly Shia), Buddhists (primarily Tibetan Buddhists), and Hindus.
- Monasteries dot the landscape, and Ladakh is famous for its vibrant festivals and rich cultural heritage⁴.
4. **Tourism and Adventure**:
- Since the 1970s, the Indian government has actively promoted tourism in Ladakh.
- Visitors are drawn to its high-altitude landscapes, pristine lakes, and ancient monasteries.
- Adventure enthusiasts flock here for trekking, river rafting, and mountaineering.
- Leh Palace, perched atop a hill, offers panoramic views of the city and surrounding mountains².
5. **Climate and Lifestyle**:
- Ladakh experiences a cold and dry climate, with extreme temperature variations.
- The main sources of livelihood are agriculture, animal husbandry, and tourism.
- The region's sparse population includes pastoral Changpa nomads who inhabit the mountain slopes⁴.
6. **Remembering Chang La**:
- Speaking of mountain passes, one of the most famous is Chang La.
- Chang La, at an elevation of 5,360 meters (17,590 feet), is known for its breathtaking views and challenging terrain.
- It's a gateway to the Nubra Valley and Pangong Lake, both must-visit destinations in Ladakh³.
So, whether you're dreaming of exploring ancient monasteries, embarking on a thrilling trek, or simply soaking in the awe-inspiring landscapes, Ladakh awaits with open arms!
Ah, Ladakh! 🏔️ The very name conjures up images of rugged mountains, serene monasteries, and vast open landscapes. Let's dive into this fascinating region:
**Ladakh: The Roof of the World**
Ladakh, often referred to as "the roof of the world" or "the land of high passes," is a remarkable region in northern India. Here are some key points about Ladakh:
1. **Geography and Borders**:
- Ladakh is situated in the northern and eastern part of the Indian subcontinent, bordering Tibet (China), Pakistan, and the Indian state of Himachal Pradesh.
- It extends from the Siachen Glacier in the Karakoram range to the north, all the way to the main Great Himalayas in the south.
- The eastern end includes the uninhabited Aksai Chin plains, which are claimed by India but have been under Chinese control.
- Ladakh's strategic location at the crossroads of important trade routes historically contributed to its significance⁴.
2. **Administration and Status**:
- Since October 2019, Ladakh has been administered as a union territory of India.
- The region comprises two districts: Leh and Kargil.
- Leh, the largest town, serves as the district headquarters.
- Ladakh's official languages are Hindi and English, while Ladakhi, Purgi, Shina, and Balti are also spoken⁴.
3. **Culture and Religion**:
- Ladakh is a melting pot of diverse cultures and religions.
- The main religious groups include Muslims (mainly Shia), Buddhists (primarily Tibetan Buddhists), and Hindus.
- Monasteries dot the landscape, and Ladakh is famous for its vibrant festivals and rich cultural heritage⁴.
4. **Tourism and Adventure**:
- Since the 1970s, the Indian government has actively promoted tourism in Ladakh.
- Visitors are drawn to its high-altitude landscapes, pristine lakes, and ancient monasteries.
- Adventure enthusiasts flock here for trekking, river rafting, and mountaineering.
- Leh Palace, perched atop a hill, offers panoramic views of the city and surrounding mountains².
5. **Climate and Lifestyle**:
- Ladakh experiences a cold and dry climate, with extreme temperature variations.
- The main sources of livelihood are agriculture, animal husbandry, and tourism.
- The region's sparse population includes pastoral Changpa nomads who inhabit the mountain slopes⁴.
6. **Remembering Chang La**:
- Speaking of mountain passes, one of the most famous is Chang La.
- Chang La, at an elevation of 5,360 meters (17,590 feet), is known for its breathtaking views and challenging terrain.
- It's a gateway to the Nubra Valley and Pangong Lake, both must-visit destinations in Ladakh³.
So, whether you're dreaming of exploring ancient monasteries, embarking on a thrilling trek, or simply soaking in the awe-inspiring landscapes, Ladakh awaits with open arms! 🌄✨
0 Comments
0 Shares
701 Views
0 Reviews